
DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, is the name that is defining a significant trend that has been taking place around Blockchain technology in recent years. DeFi seeks to develop small traditional financial pieces with an extra degree of transparency and decentralization.
These small pieces are combinable with each other in order to create an entire ecosystem of small solutions that together form an excellent solution for finance that negates the need for centralized and opaque financial institutions that no longer add value.
That is the idea that has driven the creation of the term “DeFi” and has led its evolution to the current point. In fact, it is currently impossible to ignore the considerable impact that DeFi has on the crypto world.
Imagine a world where anyone could create transparent, fair and efficient financial products, making banks, prominent financiers, lenders, and insurance companies into the background, or better yet, wholly unnecessary and disappear. But also a world where anyone can freely interact with these products.
Well, this is what DeFi is. In other words, it wants to convert the centralized finance structures that we have now, into decentralized networks, without trusted third parties, executed on smart contracts within a Blockchain where a written and unalterable record of each action carried out is transparently reflected.
And since the invention of the term “DeFi”, many projects have been developed under these innovations, and this article will talk about 5 examples of these DeFi projects.
But before we see these examples, let’s briefly know what DeFi is and how it works.
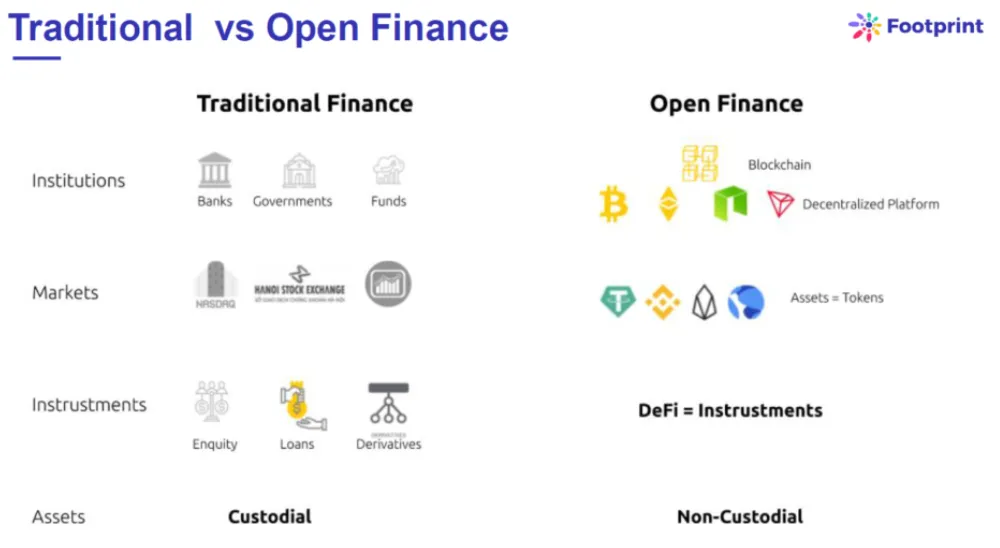
What is DeFi?
Decentralized finance is another name for DeFi. It is a cutting-edge financial model that uses smart contracts in chains of blocks, with Ethereum being the most well-known.
This approach eliminates the need for traditional financial instruments to be offered by central financial intermediaries like brokerages, exchanges, or banks. DeFi platforms enable users to save money, trade bitcoins, insure against risk, speculate using derivatives on the price movement of a range of assets, and lend or borrow money from others.
Some DeFi applications offer high-interest rates but are subject to high risk.
DeFi is a global and open financial system for the Internet age, an alternative to the outdated system, heavily controlled and maintained by processes and infrastructures of the last century.
In DeFi, you have complete visibility and control over your money. You can interact with world markets and alternatives to your country’s local currency or banking entities.
DeFi products allow the use of financial services by anyone with an Internet connection, and said services are managed and maintained by their users. So far, billions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency have circulated through DeFi applications, which continues to increase daily.
DeFi is an umbrella term for any Ethereum user or anyone with an Internet connection who can access a wide range of financial products and utilities.
Since there are no centralized agents to obstruct transactions or deny entry to any of the services, DeFi’s markets are always open. These services, previously slow and at risk of human error, are now automatic and more secure because they are driven by code that anyone can inspect and analyze.
DeFi is part of a system whereby financial products are made available on a public Blockchain network, making them open, without centralized custody, and available for anyone to use.
In this way, these products do not depend on intermediaries such as commercial banks, central banks, or brokerages.
Unlike financial products held in custody by an entity (such as a bank account), access to a product in DeFi does not require a government-issued ID, social security number, or proof of address. We simply need an internet connection. With it, we can enjoy these services.
DeFi refers to a system whereby software written on Blockchain makes it possible for buyers, sellers, lenders, and borrowers to interact with peers or with a strictly software-based intermediary rather than a company or institution facilitating a transaction.
There is an apparent growing crypto economy, where you can lend, borrow, short-term and long-term, earn interest, and much more. In Argentina, for example, cryptocurrency users have managed to escape the strong inflation that affects the country through the use of DeFi.
Companies are starting to pay their employees’ salaries in real time. Some people have been known to withdraw and repay millions of dollars in loans without needing personal identification.
How Does Defi Work?
DeFi works through applications known as dApps (decentralized applications) that perform financial functions on financial records (ledgers) called Blockchains. This technology was first used by Bitcoin and has since spread widely.
Smart contract software acts as a middleman between parties to facilitate transactions rather than a centralized intermediary like a cryptocurrency exchange.
To access dApps, one typically uses a Web3 browser extension or an application such as MetaMask that allows users to operate directly with the Ethereum Blockchain through a web page.
Many of these DApps can connect and work together to create complex financial services. For example, investors in stable coins (stable coins) can send assets to a liquidity pool. Others can borrow from these pools, contributing additional collateral, usually more significant than the total amount of the loan. The protocol automatically adjusts the interest rate based on moment-to-moment demand for the asset.
The term “decentralization” refers to the absence of a centralized exchange platform. Instead, a team of developers and programmers uses open-source software to create smart contract programs for the DeFi protocols.
DeFi uses a technological Blockchain ecosystem to bypass traditional financial services management systems and processes, or “middlemen.” It uses digital wallets, smart contracts, or digital agreements and oracles to do this.
As a decentralized system, DeFi has a financial infrastructure that works with multiple computer networks that serve as public ledgers that store digital copies of transactions. It uses cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, or digital agreements on the Ethereum network, the second-largest bitcoin market.
The DeFi concept is new and is also being adapted to mortgages, loans, and other banking products. This emerging financial technology uses decentralized applications (dApps), which are made up of hardware, software, and stablecoins (stablecoins).
It allows the user to lend, borrow and trade cryptocurrencies without obtaining authorization from central banks or other government bodies.
In practice, DeFi protocols are built from smart contracts, which are self-executing programs making use of Blockchain technology to ensure compliance with the signed agreement so that operations do not need intermediaries.
Most of them are built in the Ethereum network, but many other alternatives are evolving, offering more speed and scalability at lower costs.
The rise of DeFi has made the US-based company Coinbase adapt to this concept and create a decentralized cryptocurrency exchange popularly known as the Global Digital Asset Exchange (GDAX).
5 Examples of DeFi Projects
The following are 5 examples of successful DeFi projects.
1. Maker
One of the earliest DeFi projects is Maker. Considering the overall value entailed in its smart contracts, it also ranks among the largest.
The bank would laugh you out the door if you tried to borrow money using cryptocurrency as collateral. However, irrespective of your credit score, the security of choice on Maker’s Oasis app is your cryptocurrency. To prove your creditworthiness to the exchange, you must deposit greater security than you borrow.
A variety of tokens can be deposited, and you can borrow as much as two-thirds of their combined worth. DAI tokens, an “algorithmic stablecoin” that monitors the value of the dollar 1:1, will be used as collateral for the loan. Additionally, interest will be added, just like with a typical loan.
The DAI you procure is generated and added to the total supply of tokens when you borrow it. Likewise, when you repay it, your DAI is taken out of the pool of available tokens.
Maker’s algorithm modifies the interest rates on loans to affect borrower behavior. And that is how DAI supply is controlled to maintain its value in line with the dollar.
Although algorithmic stablecoins carry some risk, DAI has consistently sustained its peg to the dollar since 2019 – except for a few minor disparities. Consider TerraUSD, for instance, which lost its peg and fell by 99% in value relative to the dollar. However, there is currently no proof that DAI would act similarly.
Maker is also the home of the Maker (MKR) token, which, similar to stocks, offers holders the opportunity to vote at shareholders’ meetings and allows them to influence how the project handles its activities.
2. Lido
One way that Blockchains safeguard transactions is through proof of stake (PoS). Users are required to front (or “stake”) their cryptocurrency as network collateral. These users are referred to as “validators.” They gain the opportunity to collect transaction fees in return.
This year, Ethereum began utilizing PoS to protect its transactions. It has long been expected, and validators have been staking ether for at least 32 tokens each on a separate “Beacon Chain” that would eventually combine with the existing Blockchain when Ethereum becomes entirely PoS.
Undoubtedly, only some have 32 ethers, or $60,000 in cash, hanging around to join the staking trend. Herein lies Lido’s role. The initiative allows you to combine your ether with other stakers, effectively eliminating the need for minimal staking.
Additionally, unlike traditional ether staking, you can withdraw your stake anytime. Lido also provides staking pools for Polkadot, Kusama, Polygon, and Solana.
Lido’s token (LDO), like that of other DeFi initiatives, offers holders a say in how the program is run.

3. Compound

In third place, we have Compound. The Compound was created in 2017 in San Francisco by Compound Labs. It is one of the first DeFi lending protocols based on the Ethereum Blockchain. Currently, it offers the possibility of operating with 9 tokens, including both cryptocurrencies and stablecoins, in a decentralized way.
Its operation is based on the fact that users who “lock” their ETH and earn interest for the time these assets are locked act as borrowers. Those who request loans pay interest and guarantee the return of the assets by collateralizing an amount that does not put the recovery at risk.
4. Curve Finance
Curve Finance is another excellent example of a DeFi project. And the majority of stablecoins trading takes place on Curve.
Why do stablecoins trade? While Tether’s US dollar stablecoin (USDT) is trading just above the dollar, DAI (algorithmic stablecoin) may be trading cents or less below the greenback. You may therefore choose to exchange your USDT for DAI. You may exchange that back into DAI if the value of DAI rises back over USDT, and so on.
You will need to know precisely what you’re doing to make money because you’ll have to pay small trading costs for the opportunity. You can also accrue interest on Curve tokens (CRV) by giving the protocol liquidity.
You will receive a portion of the trading commissions paid by other traders when you invest stablecoins and other digital assets. Depending on the kind of asset you deposit, you will know precisely how much that is.
5. Hex (HEX)
Hex is the first Blockchain certificate of deposit focused on high-interest payments.
It has a total value of $13.93 billion, but the current supply data is unclear, and therefore the market capitalization is challenging to calculate.
According to Coinmarketcap, HEX has $38.6 billion of market capitalization, which would result in an MCap/TVL of ~2,771.
This is the only token on the list that would likely be overvalued and could see devaluation in the future if its TVL (total value of all assets) did not increase.
It is noteworthy that HEX is a controversial token, commonly accused of being a scam due to its similarities to other projects revealed as Ponzi schemes.
Conclusion
Given this, there is no doubt that DeFi and its different applications will be increasingly important in the future. After all, we are only exploring these tools and acknowledging their scope.
The impact of a trend like this is gigantic. We are only in its early years, and already the creativity of the global community is shaping alternative versions of almost all existing financial products.
DeFi has exciting possibilities and has the capacity to build a financial infrastructure that is genuinely open, transparent, and unchangeable. Everyone can confirm that all transactions and data are easily accessible for users and researchers to evaluate, thanks to DeFi’s protocols and applications.
DeFi might cause a fundamental change in the financial sector and help build a more reliable, accessible, and open economic infrastructure.
See you soon,
Scaling Parrots
